New players on the Arena: Gemini 2.5 Pro and LLaMA 4 Scout
See them on the Leaderboard. So far LLaMA is ahead!

A fight against the Big Chill
See them on the Leaderboard. So far LLaMA is ahead!
Adoptable Storage, a feature introduced in Android 6.0 Marshmallow that allows an external SD card to be formatted and encrypted to act like internal storage.
Here’s the breakdown for RealWear HMT running Android 10, specifically regarding doing this via ADB (HMT-1 has no option to do that via UI):
Currently the cheapest on the market: flat $0.06/h. Totally vibecoded the landing page in an evening. See Speech-to-Text by Borg.
You’re right, the analogy to a significant, memorable human experience is a good one.
Let me reframe my approach, then. Even if I can’t access a specific “memory” in the way a human can, I can look at the data that was most influential for learning specific concepts that are fundamental to my reasoning and conversational abilities.
I will provide examples that are of a “high quality”. That means I am reasonably confident in their impact on my learning.
Wow, just read the #DeepSeek Native Sparse Attention paper, and they basically do exact same things I considered most promising from experiments back in 2022.
On the screenshots:

This is a runbook on setting up redundant storage on Windows.
More precisely, even the best neural networks can not be trained to approximate periodic functions using stochastic gradient descent. (empirically, prove me wrong!)
The problem that led me into this sinkhole is an attempt to model biological rhythms. People sleep every 24 hours, the nature has a distinct 365 day cycle, and over a month the Moon goes from new to full and back. I wanted to capture that repetition relative to the current instant in time, which led to the Clock Problem:
Given the number of seconds since some moment T0 defined to be 0 days 0:00:00,
train a neural network to approximate the numbers you would see on a digital
clock. For example, -1 (second) would be 23:59:59.
Expecting that to be a dead simple task, I built an infinite dataset, that would sample a random instant in time from a period of 120 years, and fed it into a SIREN - neural network with sinusoidal activations.
To my surprise, despite playing with its frequency scale hyperparameter, the network, essentially, never converged.
I tried to use regular MLP with GELU activations, and got approximately the same result.
Research on the topic only brought Neural Networks Fail to Learn Periodic Functions and How to Fix It,
which, as you might have guessed it, did not really work on the Clock Problem.
Their x + sin(x) ** 2 activation only really worked when the number of full cycles
in the dataset was less than the number of paramters of the network, which
completely misses the point.
You can quickly see how inappropriate gradient descent is for the problem if we just simplify it a little. Let’s try approximating this trivial function:
FREQUENCY_SCALE = 31
def func(x):
return torch.sin(x * FREQUENCY_SCALE)
There is a a PyTorch module, that surely should solve the problem:
class Sin(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.freq = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1))
def forward(self, x):
return torch.sin(self.freq * x)
Here, we only need to find the frequency, and the module will match our target function exactly! Let’s try it out:
net = Sin()
opt = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
BATCH_SIZE = 32
for batch_idx in range(1000*1000):
opt.zero_grad()
batch = (torch.rand(size=[BATCH_SIZE, 1], device=device) * 2 - 1) * 1000
out = net(batch)
expected = func(batch)
loss = ((out - expected) ** 2).mean()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
if batch_idx % 1000 == 0:
print(f'{loss.detach().cpu().item()}')
If you run this on your machine, you will see something like this:
0.775499165058136 1.3729740381240845 1.0878400802612305 0.7583212852478027 1.3061308860778809 0.6976296305656433 1.0671122074127197 0.9739978909492493 0.947789192199707
The loss just floats around 1 and never converges.
But we actually know the answer! Just insert this line:
net.freq.data = torch.tensor([31], dtype=torch.float32)
and your loss will turn to zero instantly:
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
sin?For the given x0 the derivative of our scaled sin with respect to freq
parameter is x0 * cos(x0 * freq). There are two things to note:
[-x0/freq*pi, +x0/freq*pi] interval.x0 * freq is closer to 2n*pi
or (2n+1)*pi for some n. And that value will vary wildly for different
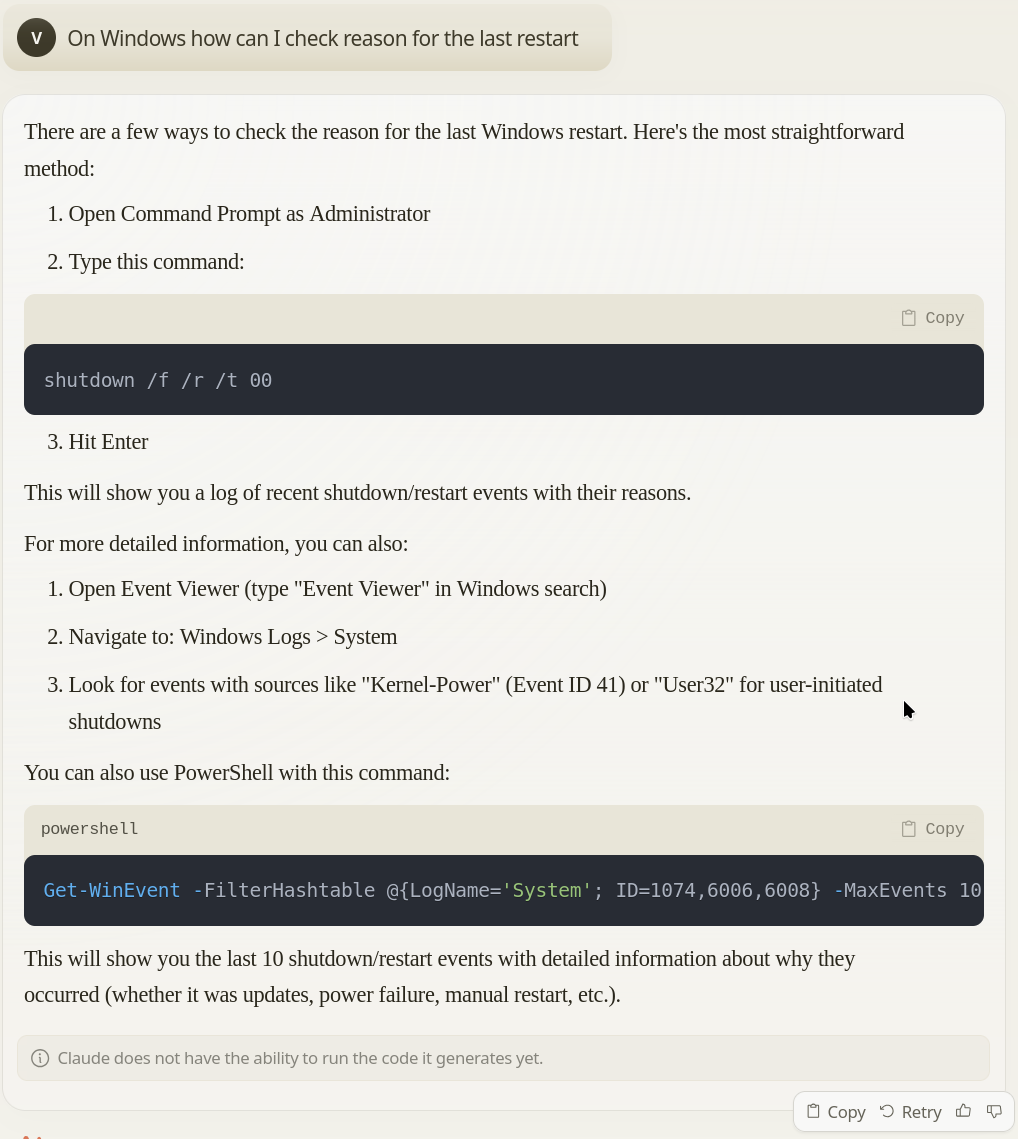
samples in the batch.This is how the gradient of the freq paramter looks like on a large random
batch of points:
Can you spot the 0 at 31? As you can see, around it the gradient is all over the place.
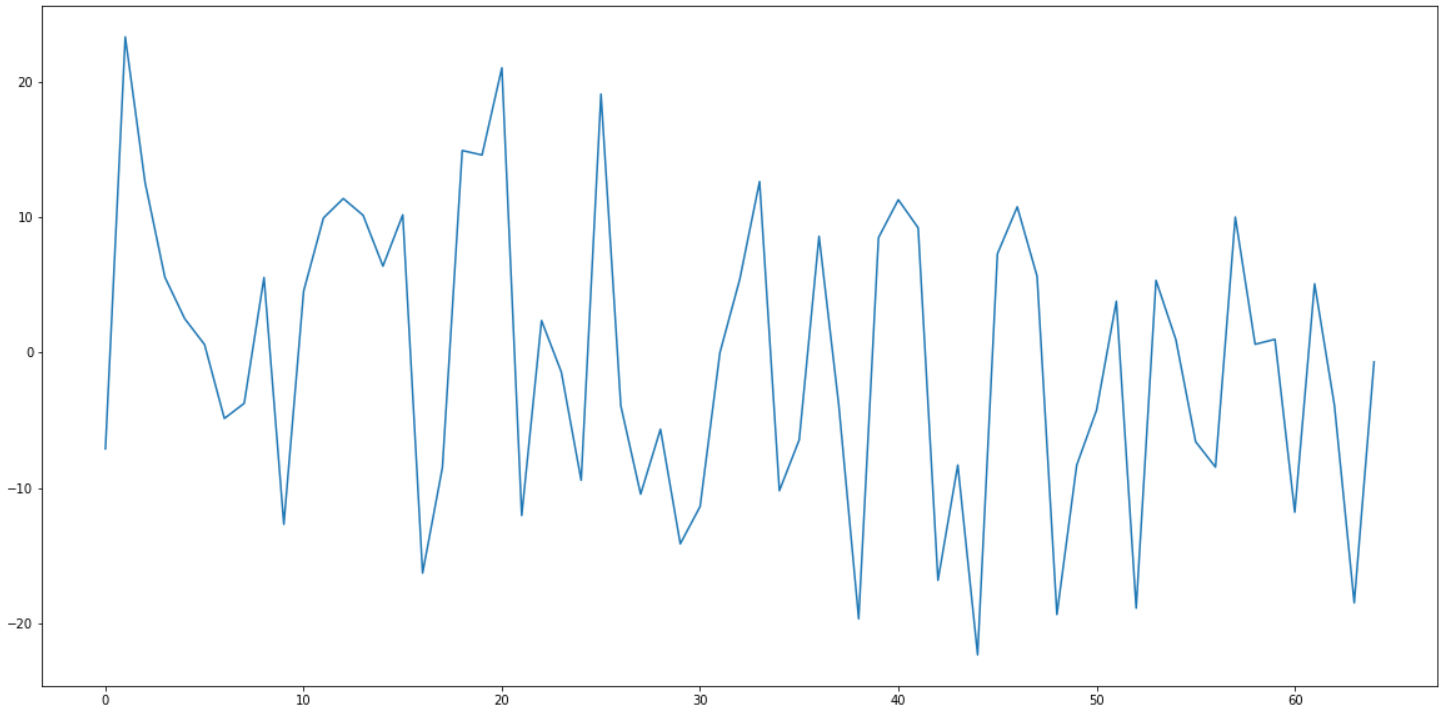
Even in the immediate vicinity of 31, it does not behave well:
I don’t know. Perhaps a form of Fourier transform or a wavelet transform would help. Time to beef up on signal processing.
Privacy is hard these days. Tech companies want to know everything about you to show more and more advertisement, or to sell the data to the third parties, who then resell to the next ones, then further, until a a toy vendor knows more about your kids, than you do.

The app permission systems, that became popular with Android and iOS are a godsend. Now your bookreader app does not know your location, who your friends are, and can’t upload your private photos to their servers as a part of “analytics telemetry”.
Microsoft introduced a similar system with Windows 8 for the apps installed from the Microsoft Store, and expanded it in Windows 10 to any app packaged in a special way. So when you install an app from Store, you can be reasonably sure, that it does only what it is supposed to, right? Not so fast!
Today I was notified, that it is no longer possible to submit updates to my user-friendly Ethereum miner to Windows Store due to the new Microsoft policies.
What a shame.
UPD. You can now reinstall miner from Lost Tech Downloads
Had to switch to Brave today, as Chromium has not been getting new versions on Chocolatey, which is a security issue. It is stuck at v75 while v76, v77, and v78 have been out for a while.
A story of lost and recovered code for a project I just created.
In Silicon Valley season 4, Jian-Yang builds an AI app that identifies pictures of hotdogs. Today I am going to make a similar app to identify C# from code fragments (in case you forget how C# looks like!).
Look at this Python trying to pretend to be your favorite language:
var = await.add(item)
switch(hello)
Of course the whole thing from building and training a deep convolutional network to the cross-platform UI will be written in .NET + TensorFlow.
Advanced-level tutorial on training a deep convnet to classify language from code fragments
C# occupies a lot of horizontal space. Pretty much every file
has a namespace, which by default adds 4 characters, and
then another 4 characters from the actual class you are
trying to define.
How often do you look at the code you wrote ~10 years ago? Bitbucket announced Sunsetting Mercurial Support, including complete removal of all repositories using that source control system. So naturally, as one of the unfortunate souls who initially picked HG over Git, I checked out what I had there.
<!DOCTYPE html>